Synopsis Visualize an Algebraic Datatype as a tree.
Description In ColoredTrees we have discussed the Algebraic Data Type
ColoredTree.
Here we show how to create a visualization for them. The global approach is:
- Define a function
visColoredTreethat has a ColoredTree as argument and creates aFigurefor it. - Display the resulting figure using Rascal:render.
Examples Here is our solution:
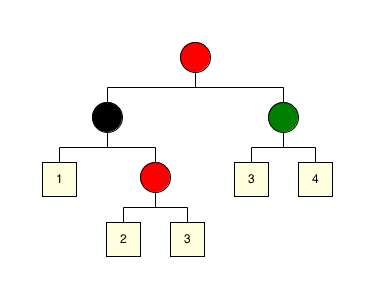
Note that:
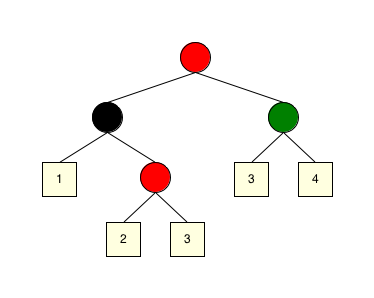
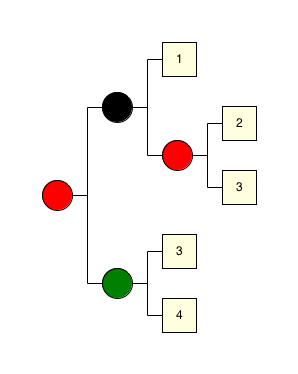
It is also possible to change the Rascal:orientation of the tree and draw it, for example, from left to right:
@license{
Copyright (c) 2009-2013 CWI
All rights reserved. This program and the accompanying materials
are made available under the terms of the Eclipse Public License v1.0
which accompanies this distribution, and is available at
http://www.eclipse.org/legal/epl-v10.html
}
module demo::vis::VisADT
import vis::Figure;
import vis::Render;
data ColoredTree = leaf(int N)
| red(ColoredTree left, ColoredTree right)
| black(ColoredTree left, ColoredTree right)
| green(ColoredTree left, ColoredTree right)
;
public Figure visColoredTree(leaf(int N)) =
box(text("<N>"), gap(2), fillColor("lightyellow"));  public Figure visColoredTree(red(ColoredTree left, ColoredTree right)) =
visNode("red", left, right);
public Figure visColoredTree(red(ColoredTree left, ColoredTree right)) =
visNode("red", left, right);  public Figure visColoredTree(black(ColoredTree left, ColoredTree right)) =
visNode("black", left, right);
public Figure visColoredTree(green(ColoredTree left, ColoredTree right)) =
visNode("green", left, right);
public Figure visNode(str color, ColoredTree left, ColoredTree right) =
public Figure visColoredTree(black(ColoredTree left, ColoredTree right)) =
visNode("black", left, right);
public Figure visColoredTree(green(ColoredTree left, ColoredTree right)) =
visNode("green", left, right);
public Figure visNode(str color, ColoredTree left, ColoredTree right) =  tree(ellipse(fillColor(color)), [visColoredTree(left), visColoredTree(right)]);
public ColoredTree rb = red(black(leaf(1), red(leaf(2),leaf(3))), green(leaf(3), leaf(4)));
tree(ellipse(fillColor(color)), [visColoredTree(left), visColoredTree(right)]);
public ColoredTree rb = red(black(leaf(1), red(leaf(2),leaf(3))), green(leaf(3), leaf(4)));
- A
leafis represented as its number converted to text, surrounded by a lightyellow box ( ).
). - The figure for non-leaf nodes of a ColoredTree is generated by the auxiliary function
visNode( ).
). -
visNoderepresents the node itself as a Rascal:tree that has a colored ellipse as root and the visualization of two ColoredTrees as children ( ).
).
ColoredTree rb we can set a standard (see Rascal:std) Rascal:size and standard Rascal:gap:
import demo::vis::VisADT; render(space(visColoredTree(rb), std(size(30)), std(gap(30))));and the result is:

Note that:
- We place the Figure that is produced by
viscoloredTreein aspacefor the sole purpose that add extra proerties to it. - We use
std(size(30))andstd(gap(30))to achieve that these properties are set for all subfigures.
import demo::vis::VisADT; render(space(visColoredTree(rb), std(size(30)), std(gap(30)), std(manhattan(false))));the result is:

It is also possible to change the Rascal:orientation of the tree and draw it, for example, from left to right:
import demo::vis::VisADT; render(space(visColoredTree(rb), std(size(30)), std(gap(30)), std(orientation(leftRight()))));the result is:
