Synopsis Abstract syntax for Pico.
Examples Here is the complete abstract syntax for Pico:
module demo::lang::Pico::Abstract public data TYPE = natural() | string();Notes:public alias PicoId = str;
public data PROGRAM =
program(list[DECL] decls, list[STATEMENT] stats); public data DECL = decl(PicoId name, TYPE tp); public data EXP = id(PicoId name) | natCon(int iVal) | strCon(str sVal) | add(EXP left, EXP right) | sub(EXP left, EXP right) | conc(EXP left, EXP right) ; public data STATEMENT = asgStat(PicoId name, EXP exp) | ifElseStat(EXP exp, list[STATEMENT] thenpart, list[STATEMENT] elsepart) | whileStat(EXP exp, list[STATEMENT] body) ; anno loc TYPE@location;
anno loc PROGRAM@location; anno loc DECL@location; anno loc EXP@location; anno loc STATEMENT@location; public alias Occurrence = tuple[loc location, PicoId name, STATEMENT stat];

-
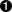 The types that may occur in a Pico program are either natural or string.
The types that may occur in a Pico program are either natural or string. -
 Introduce
Introduce PicoIdas an alias for Rascal'sstrdatatype. -
 Define the various data types that constitute an AST for Pico. Observe that the constructor names match the names used in the concrete syntax, e.g.,
Define the various data types that constitute an AST for Pico. Observe that the constructor names match the names used in the concrete syntax, e.g., strCon,add,ifElseStat. -
 Define an annotation with name
Define an annotation with name locationand of typeloc(source code location) for all AST types. This will be used when imploding a parse tree into an abstract syntax tree. -
 Introduce
Introduce Occurrenceas a genereic way of describing the location of various items in the AST.